Relationship in life holds an exceptional place. Marriage is a relationship that plays a vital role...
Category - Editorial
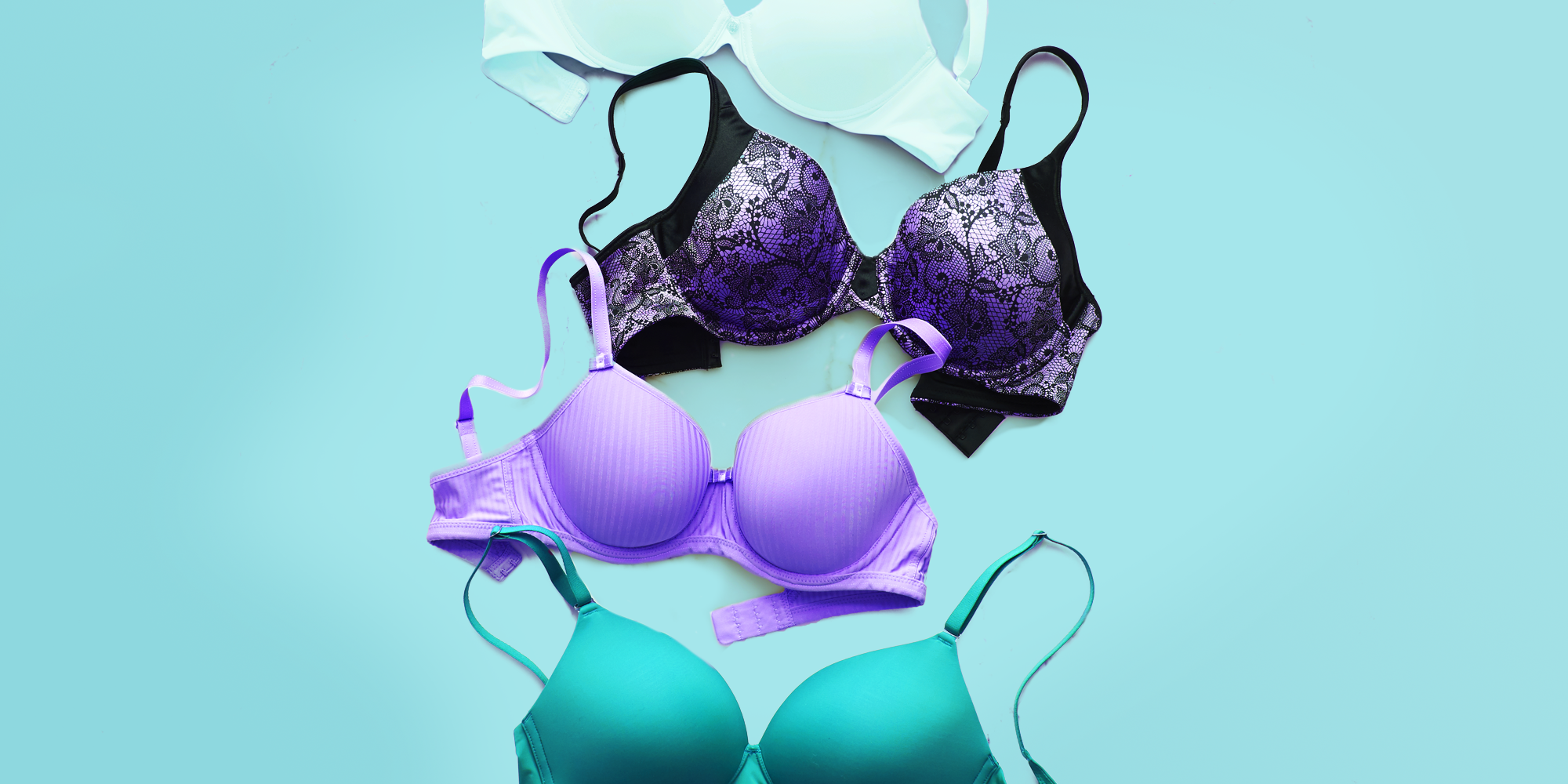
Types of Bras
Types of Bras Bras are considered as one of the most practical inventions for women across history...
Summer Makeup Essentials
With the scorching sun and an intense hot temperature, all you need is comfortable attire, relaxing...
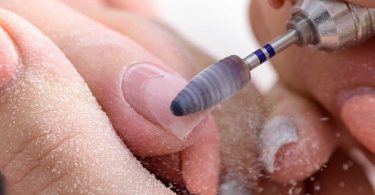
How to Remove Acrylic Nails?
How to Remove Acrylic Nails? Are you fond of having acrylic nails? Well if you do so then you must...
How To Get Rid Of Double Chin?
How to get rid of a double chin? Everyone loves to look beautiful and flawless skin. When you see a...
How to get back in the dating game after taking a break?
How to get back in the dating game after taking a break? Trauma and pain has lasting effect on ones...